Ca Oh 2 Equilibrium Equation
The hydroxide ion is a natural part of water because of the self-ionization reaction in which its complement hydronium is passed hydrogen. The products formed are water and salt.

Equilibrium Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 7 11th Chemistry Chemistry Chemistry Lessons
Chukanov Stefano Merlino Vasiliy O.

. Solid liquid and gas. Lets move left to right on the graph. Click to see the answer.
A double replacement reaction will occur if a formation of a precipitate gas or water takes place. Just dissolved CO 2Essentially at 43 pH carbonic acid the red line begins to transition into bicarbonate the green line. In which direction toward reactants or toward products does the reaction shift if the equilibrium is stressed by each change.
The equilibrium constant Kc for the following reaction is 18010-2 at 698 K. 16 In 1925 pK 1 and therefore pH was shown to be influenced by ionic strength μ 17 and temperature 18 the ΔpK 1 K 1 K 1. Select two compounds above and this calculator will predict whether or not the reaction will occur in waterThis is simply based on the solubility chart of inorganic compounds.
B OH 9⁰H 1 Br₂ PBr3 2 H₂O. As you may know when an acid or a base dissolves in water their H and OH ions respectively dissociate shifting the natural self-ionisation equilibrium of water 2H₂O H₃O OH making the solution more acidic or more basic. The H and OH- react to form H2O.
The equation for the reaction is shown. A050 mol dm 3 B10 mol dm 3 C20 mol dm 3 D40 mol dm 3. N 2 3H 2 2NH 3.
Anything below 43 pH there is zero alkalinity in the water. What is the concentration of the dilute sulfuric acid in mol dm3. At pH 7 the concentration of H₃O ions to OH ions is a ratio of 11 the equivalence point.
Given this reaction at equilibrium. Paratobermorite Ca 4 Al 05 Si 05 2 Si 4 O 16 OH2H 2 OCa3H 2 O a new tobermorite-supergroup mineral with a novel topological type of the microporous crystal structure Igor V. A neutralization reaction is when an acid and a base react to form water and a salt and involves the combination of H ions and OH-ions to generate water.
NH 3 is removed. However an online Chemical Equation Balancer Calculator will provide you the balanced equation equilibrium constant with chemical name and formula of all reactants and product of a chemical equation. Strong Acid-Strong Base Neutralization.
If H 2 is added there is now more reactant so the reaction will shift toward products to reduce. Carbonic acid is dissolved carbon dioxide CO 2. Neutralization reactions are the reaction between acid and base.
Such pH-dependent solubility is not restricted to salts that contain anions. When multiplying or dividing numbers round the result to the same number of total digits the same relative precision as the input value with the fewest significant figures. Pool chemistry should range between 72 and 82.
A OH 1 Br₂ PBr3 2 H₂O. It is called so because the acid and base neutralize each other to form water and salt. Learn more about the Neutralization Reaction here.
P 7 41 11. K w H OH. NH 3 is added.
2HIg H2g I½g. 6 This finding shows that the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation cannot be accurately applied to mammalian blood cooled in. The overall equation for the reaction of MgOH 2 with acid is thus MgOH_2s 2H aq rightleftharpoons Mg2 aq 2H_2O l label1717 As more acid is added to a suspension of MgOH 2 the equilibrium shown in Equation ref1717 is driven to the right so more MgOH 2 dissolves.
In the example above our least precise input value has three significant figures 101 so the answer to the calculation should also have three significant figures. The neutralization of a strong acid and strong. Has a value close to 10 14 at 25 C so the concentration of hydroxide ions in pure water is close to 10 7 moldm.
It was evident as early as 1922 that factors other than P co 2 HCO 3 pK 1 and S influence plasma pH. H 2 is added. Q3 Covalent bonded materials are found in all three states.
By making considerable change in enthalpy equation we get. 2NaOH H 2 SO 4 Na 2 SO 4 2H 2 O The reaction requires 500 cm3 of dilute sulfuric acid to reach the end-point. P ΔH ΔQ ΔV.
Weak Acid-Weak Base Neutralization. Solution for Clear All strong acid CaOH2 weak acid NH3 strong base HNO2 weak base KCI soluble salt H2CO3 insoluble salt. H 3 O OH 2H 2 O.
A chemical equation is the symbolic representation of a chemical reaction in the form of symbols and formulae wherein the reactant entities are given on the left-hand side and the product entities on the right-hand side with a plus sign between the entities in both the reactants and the products and an arrow that points towards the products and shows the direction of the reaction. 43 pH is the point where alkalinity begins to exist in water. The equilibrium constant for this reaction defined as.
Solution for 2110 Predict the major product for each of the following transformations.

Pin On Cbse Class 11th Physics Notes

Equilibrium Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 7 11th Chemistry Chemistry Chemistry Lessons

20 Science Fair Award Certificate In 2020 Science Within Science Award Certificate Templa Science Awards Certificate Templates Awards Certificates Template

Strong Acids And Bases Mcat Chemistry Cheat Sheet Study Guide Studypk Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Lessons Chemistry Basics
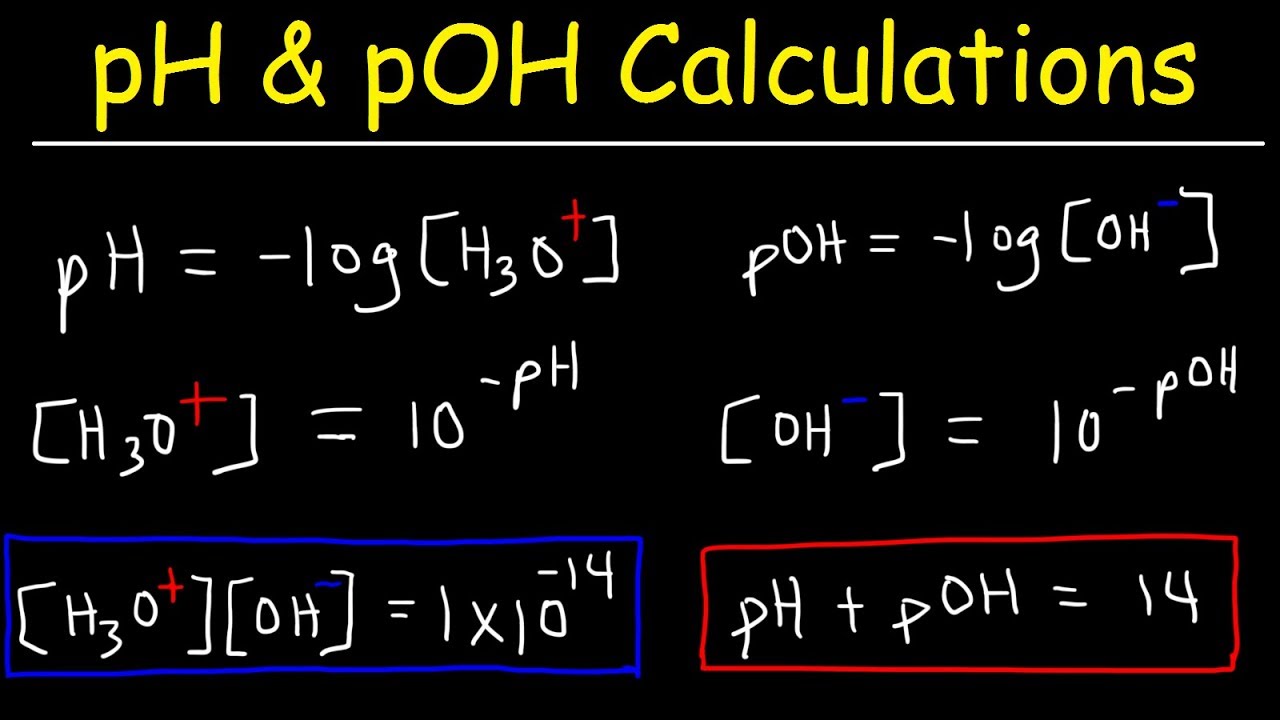
Ph Poh H3o Oh Kw Ka Kb Pka And Pkb Basic Calculations Acids And Bases Chemistry Problems Chemistry Lessons Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Classroom

Comments
Post a Comment