Carbohydrates Promote Dental Caries by Which of the Following Mechanisms
Two important findings were noted. All of these choices are correct.
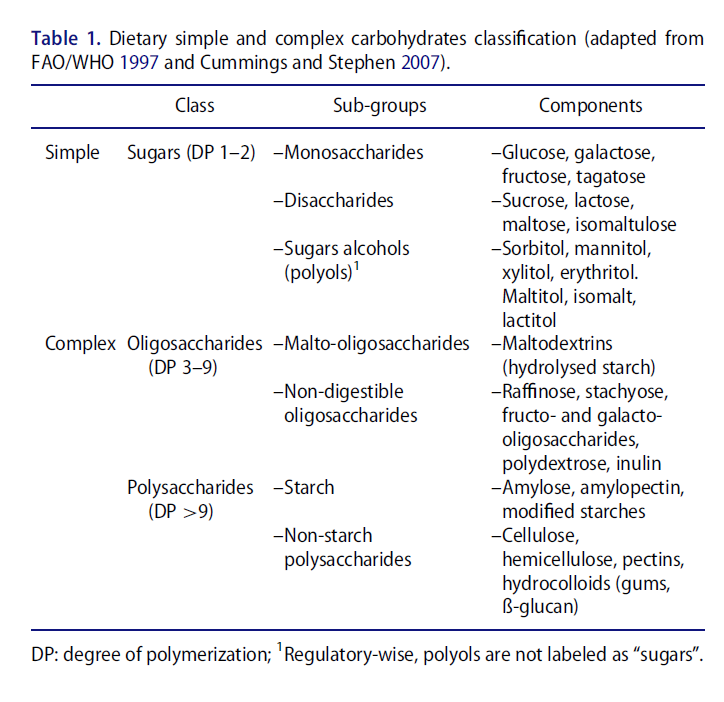
The Scientific Basis For Healthful Carbohydrate Profile
Caries can occur in absence of proteolytic organisms.

. Glass RL Fleisch S 1974 Diet and caries. The aetiology of caries is multifactorial and involves host factors such as salivary components. This produces acid as a byproduct which reduces the pH of the environment around dental structures.
Cariogenic bacteria which mainly include streptococci mutans and lactobacilli metabolize carbohydrates by fermentation. Clinical and radiographic examination reveal tooth 47 has. Dental caries is an infectious disease that results in demineralization of the tooth and the formation of cavities.
The proximal surfaces of two adjacent teeth in contact form the borders of the The effects of polymerization shrinkage of composite resin must be taken into account for all the following EXCEPT the placement of aan A patient presents with pain from tooth 47 which is an abutment for a 4 unit bridge from 44 to 47. In the case of human dental caries the presence of excess carbohydrates is often responsible for altering the local environment to be. The bacteria responsible produce organic acids as a by-product of their.
These bacteria live in bacterial communities known as dental plaque which accumulates on the tooth surface. Dental Caries Decay Dental decay is due to the dissolution of tooth mineral primarily hydroxyapatite Ca 10 P0 4 6 0H 2 by acids derived from bacterial fermentation of sucrose and other dietary carbohydrates. Bacteria metabolize carbohydrate to form acids which break down enamel Carbohydrates provide 60 percent of the energy in Jimmy Johns diet of 2700 kilocalories.
According to our knowledge base today fluoride works to prevent and control dental caries through the following two primary mechanisms that affect 1 enamel solubility and 2 reversal of the caries process. 1974 Diet patterns and dental caries in third grade. Sugar promotes the growth of bacteria that breakdown enamel.
Carbohydrates promote dental caries by which of the following mechanisms. The primary microbial agent in caries is the Gram-positive facultative. The pH of dental plaque under resting conditions ie when no food or drink has been consumed is fairly constant.
Dryness of the mouth caused by abnormal reduction in the amount of saliva. Organic acids increase the solubility of calcium hydroxyapatite in dental hard tissues and demineralization. The thin coating of salivary materials that are deposited on tooth surfaces.
Dental plaque is the main cause of primary and secondary dental caries and gingivitis adjacent to teeth. Carbohydrates stick to teeth preventing the removal of plaque. US Food Guide Pyramid and Dietary Guidelines for Americans along with the European National Guidelines 34 68 promote a diet rich in carbohydrates.
J Am Dent Assoc 88807813. Up to 24 cash back Acidogenic bacteria in dental plaque rapidly metabolize fermentable carbohydrates producing acidic end products. Carbohydrates promote dental caries by which of the following mechanisms.
B A systemic effect during the period of tooth development where fluoride is incorporated into the enamel during its formation. Dental caries occurs due to the demineralization of enamel and dentin the hard tissues of the teeth by organic acids formed by bacteria in dental plaque through the anaerobic metabolism of sugars and other fermentable carbohydrates derived from the diet. In the mouth these changes over time in response to a challenge are known as Stephan responses or Stephan curves.
First dental caries appeared to be influenced more by frequency of sucrose intake than by total amount consumed. Dental caries is a transmissible bacterial disease process caused by acids from bacterial metabolism diffusing into enamel and dentine and dissolving the mineral. The nature of the oral cavity and host behaviors has mandated that the oral microbiota evolve mechanisms for coping with environmental fluctuations especially changes in the type and availability of carbohydrates.
Bacteria metabolize carbohydrate to form acids which break down enamel. Dietary factors such as the availability of fermentable carbohydrate. Dental caries is a biofilm-mediated sugar-driven multifactorial dynamic disease that results in the phasic demineralization and remineralization of dental hard tissues.
Dental caries incidence and the consumption of ready to eat cereals. An oral infectious disease of the teeth in which organic acid metabolites produced by oral microorganisms lead to demineralization and destruction of the tooth structures. Although sugars are undoubtedly the most important dietary factors in the etiology of dental caries todays diet contains an increasing range of fermentable carbohydrates including highly processed starch-containing foods and foods that contain novel synthetic carbohydrates such as oligofructose sucralose and glucose polymers.
However Proteolytic bacteria are rare in oral cavity No explanation for role of carbohydrates acid etc in dental caries Carious lesions cannot be reproduced in vitro by the proteolytic mechanisms Gnotobiotic studies. Dental caries is one of the most prevalent conditions worldwide and accounts for significant morbidity Importantly the prevalence of untreated dental caries has increased 1 2While there is a direct effect of untreated dental caries on oral health and associated quality of life identification of indirect associations between dental caries. PubMed CAS Google Scholar Bagramian RA et al.
The main mechanism by which fluoride protects against dental caries is. Second solid forms of sugar which are more easily retained in teeth appear to be more cariogenic than liquid forms of sucrose Gustafsson et al 1952. A An intra oral topical effect by which fluoride is incorporated into the enamel during remineralisation.

Fluoride S Mechanism Of Action Fundamentals Of Dentifrice Oral Health Benefits In A Tube Continuing Education Course Dentalcare Com
Materials Free Full Text Mechanisms Of Bioactive Glass On Caries Management A Review Html

Pdf Components Of The Diet And Its Relation To Dental Caries A Review

Dietary Carbohydrate An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Pdf The Role Of Diet And Oral Hygiene In Dental Caries

Tooth Enamel An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Fluoride S Mechanism Of Action Fundamentals Of Dentifrice Oral Health Benefits In A Tube Continuing Education Course Dentalcare Com
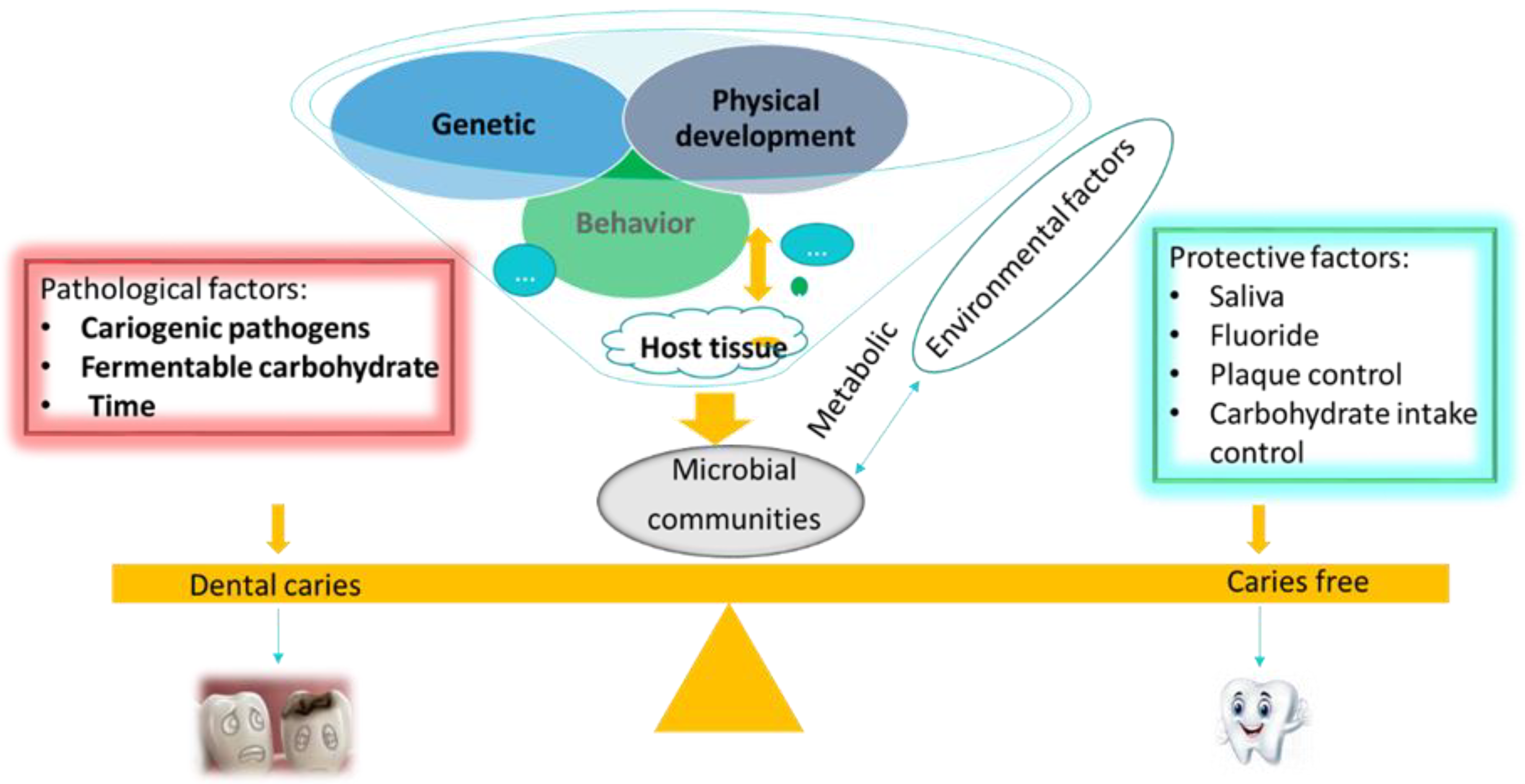
Pathogens Free Full Text Microbial Etiology And Prevention Of Dental Caries Exploiting Natural Products To Inhibit Cariogenic Biofilms Html

Positive Feedback Loop Leading To Caries In This Positive Feedback Download Scientific Diagram

References In Dental Caries The Lancet
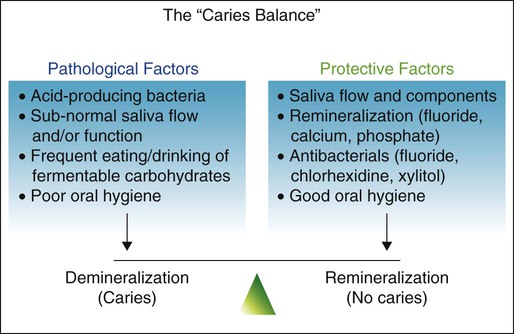
2 Dental Caries Etiology Clinical Characteristics Risk Assessment And Management Pocket Dentistry

Pdf Sugars And Beyond The Role Of Sugars And The Other Nutrients And Their Potential Impact On Caries
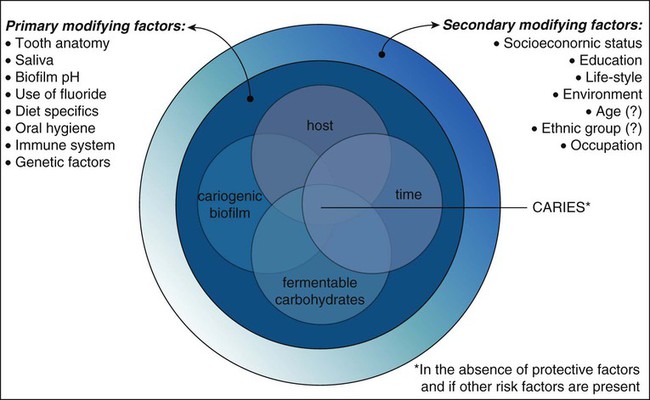
2 Dental Caries Etiology Clinical Characteristics Risk Assessment And Management Pocket Dentistry

Factors In Caries Development And The Balance Between Pathological Download Scientific Diagram

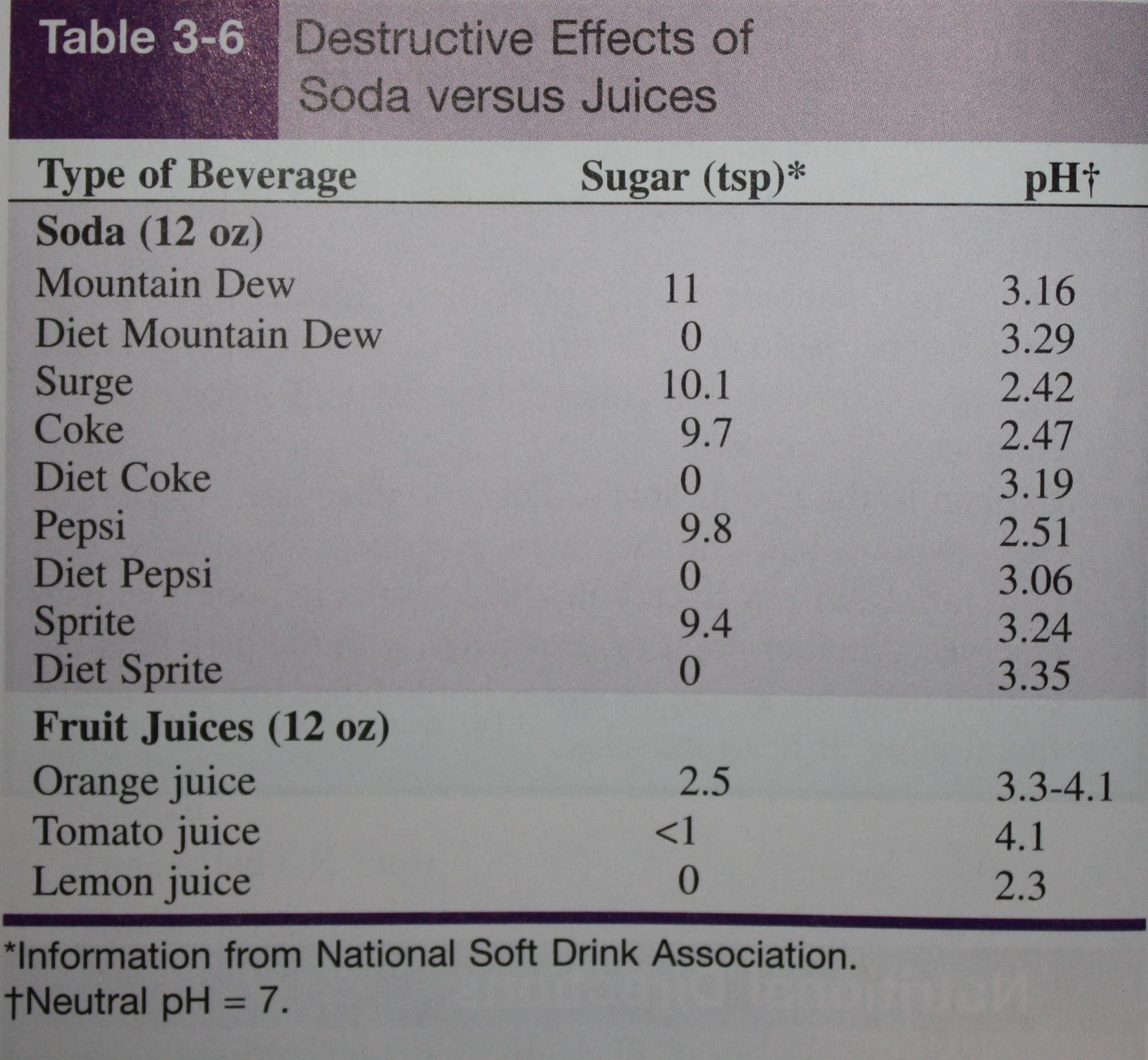

Comments
Post a Comment